Geometry is the study of shapes, sizes, and patterns in mathematics. One of the fundamental concepts of geometry is the converse, which is a statement that is logically equivalent to another statement. In this article, we will explore what a converse is and how it is used in geometry. We will also look at some examples of converses in geometry and how they can be used in problem-solving. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of the converse in geometry!
A converse in geometry is a statement that is formed by switching the hypothesis and conclusion of a given true statement. For example, if we have the statement, “If two angles are equal, then they are congruent,” then its converse would be “If two angles are congruent, then they are equal.” The converse of a statement is not necessarily true and must be proven through a proof.
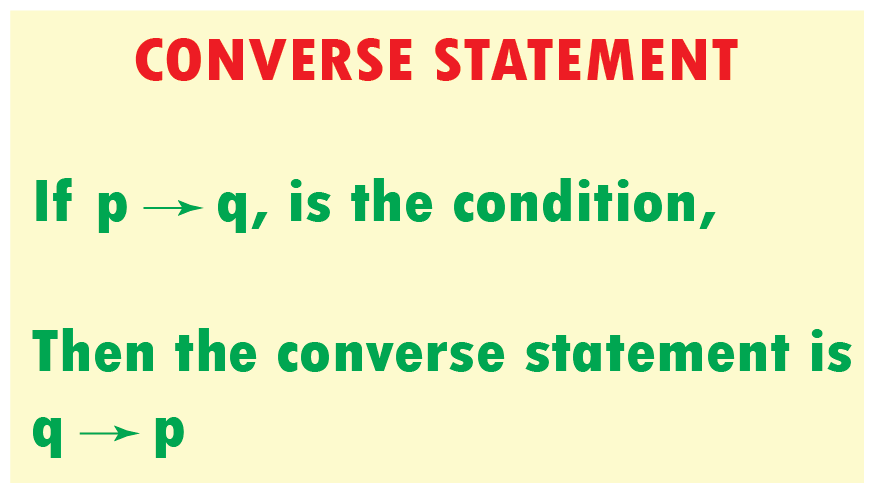
What is a Converse in Geometry?
A converse in geometry is a statement that is the opposite of a given statement. Converse statements are often used to make logical deductions or conclusions. They are also used to prove theorems that have already been established. In geometry, a converse statement can be used to prove the opposite of a given theorem or statement.
What is the Definition of a Converse?
In geometry, a converse is a statement that is the opposite of a given statement. For example, the statement “If two lines intersect then they form four angles” is the converse of the statement “If two lines form four angles then they intersect”. A converse statement is also known as the contrapositive of a given statement.
What is an Example of a Converse?
A common example of a converse statement is the statement “If two angles are congruent then the lines that form them are parallel”. This statement is the converse of the statement “If two lines are parallel then the angles that form them are congruent”.
How Can a Converse be Used in Geometry?
A converse can be used to make logical deductions or conclusions in geometry. For example, if a given theorem states that two lines that intersect form four angles, then the converse statement can be used to prove the opposite – that if two lines form four angles then they must intersect. A converse can also be used to prove theorems that have already been established.
What is the Difference Between a Converse and an Inverse?
The difference between a converse and an inverse is that a converse is the opposite of a given statement while an inverse is the negation of the statement. For example, the statement “If two lines intersect then they form four angles” is the converse of the statement “If two lines form four angles then they intersect”. The inverse of this statement is “If two lines don’t intersect then they don’t form four angles”.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Converse in Geometry?
A converse in geometry is an implication between two theorems or statements in which the antecedent and consequent are reversed. In other words, a converse is an implication between two statements where the order of the hypothesis and conclusion is switched. For example, the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem is: if the sum of the squares of two sides of a triangle is equal to the square of the third side, then the triangle is a right triangle.
What are the Different Types of Converses in Geometry?
There are two main types of converses in geometry: converses of theorems and converses of definitions. A converse of the theorem is an implication between two theorems in which the antecedent and consequent are reversed. A converse of a definition is an implication between two definitions in which the order of the two definitions is reversed.
How Do I Prove a Converse in Geometry?
In order to prove a converse in geometry, you must use logic to prove that the hypothesis and conclusion of the converse are true. The proof should begin by stating the antecedent and consequent of the converse. Then, you must use logical statements to prove that the hypothesis is true if the conclusion is true. Finally, you must use logical statements to prove that the conclusion is true if the hypothesis is true.
What is an Example of a Converse in Geometry?
A common example of a converse in geometry is the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem. The Pythagorean Theorem states that if the sum of the squares of two sides of a triangle is equal to the square of the third side, then the triangle is a right triangle. The converse of the Pythagorean Theorem is: if the triangle is a right triangle, then the sum of the squares of two sides of the triangle is equal to the square of the third side.
What is the Relationship Between the Converse and the Original Theorem?
The relationship between the converse and the original theorem is that the converse is an implication between two statements in which the order of the hypothesis and conclusion are reversed. In other words, the converse is the same statement as the original theorem, but with the antecedent and consequent reversed.
What is the Difference Between a Converse and a Contrapositive?
The difference between a converse and a contrapositive is that a converse is an implication between two statements in which the order of the hypothesis and conclusion are reversed, while a contrapositive is an implication between two statements in which the hypothesis and conclusion are both negated. For example, the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem is: if the triangle is a right triangle, then the sum of the squares of two sides of the triangle is equal to the square of the third side. The contrapositive of the Pythagorean Theorem is: if the sum of the squares of two sides of a triangle is not equal to the square of the third side, then the triangle is not a right triangle.
A converse in geometry is a type of logical statement where the inverse of a given statement is true. It is used to determine the truthfulness of a statement by comparing the original statement to its inverse. This type of statement is an important tool in geometry and can be used to prove theorems and solve problems. By understanding the concept of a converse in geometry, students can unlock many of the mysteries of the subject and improve their understanding of geometry as a whole.
